Create a RESTful API using Node and Express with MySQL Database
Node Express web framework is the best solution to create RESTful APIs in a quick time. Previously we published some concepts with different technologies like PHP and Java. This article will explain to you a more simple way to use external plugins to enrich your project APIs. Here you will find to create GET and POST requests with request payload validations to protect the endpoints.

We have already discussed how to create RESTful APIs using PHP and Java in my previous tutorials.
You have to install NodeJs and MySQL software. You will find the SQL file in the Git repository.
Users Table
User table contains all the user's registration details.
CREATE TABLE `users` (
`uid` int(11) AUTO_INCREMENT,
`username` varchar(50),
`password` varchar(200),
`email` varchar(200),
PRIMARY KEY (`uid`)
);
`uid` int(11) AUTO_INCREMENT,
`username` varchar(50),
`password` varchar(200),
`email` varchar(200),
PRIMARY KEY (`uid`)
);
Table Messages
This table contains all of the user messages.
CREATE TABLE `messages` (
`mid` int(11) AUTO_INCREMENT,
`message` text,
`uid_fk` int(11),
PRIMARY KEY (`mid`)
);
`mid` int(11) AUTO_INCREMENT,
`message` text,
`uid_fk` int(11),
PRIMARY KEY (`mid`)
);
Initialize NodeJS
Create a project folder and initialize the Node project.
$npm init
This will generate a package.json with product information. Give starting file as src/index.js.
About to write to /Users/SrinivasTamada/Desktop/projects/Node-Express-MySQL-Restful/package.json:
{
"name": "node-express-mysql-restful",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "Node express MySQL restful api",
"main": "src/index.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"repository": {
"type": "git",
"url": "git+https://github.com/srinivastamada/Node-Express-MySQL-Restful.git"
},
"keywords": [
"Node",
"Express",
"MySQL",
"Restful"
],
"author": "Srinivas Tamada",
"license": "ISC",
"bugs": {
"url": "https://github.com/srinivastamada/Node-Express-MySQL-Restful/issues"
},
"homepage": "https://github.com/srinivastamada/Node-Express-MySQL-Restful#readme"
}
Is this OK? (yes) y
{
"name": "node-express-mysql-restful",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "Node express MySQL restful api",
"main": "src/index.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"repository": {
"type": "git",
"url": "git+https://github.com/srinivastamada/Node-Express-MySQL-Restful.git"
},
"keywords": [
"Node",
"Express",
"MySQL",
"Restful"
],
"author": "Srinivas Tamada",
"license": "ISC",
"bugs": {
"url": "https://github.com/srinivastamada/Node-Express-MySQL-Restful/issues"
},
"homepage": "https://github.com/srinivastamada/Node-Express-MySQL-Restful#readme"
}
Is this OK? (yes) y
Install Dependencies
You have to follow Node dependencies to improve the project.
Express
Express is a web application framework, that provides restful endpoints.
npm install express
MySQL
This helps you connect the MySQL database. Install XAMPP for the MySQL database.
npm install mysql
Nodemon
Nodemon is a tool that helps to Node application continuously.
npm install nodemon
.gitignore
Create a ignore file for Git and exclude node_modules.
/node_modules
.prettierrc
Prettier configuration file. Here I have enabled singleQuote value true
{
}
"singleQuote": true
Project Structure
Create a folder src and create two blank JavaScript files index.js and queries.js

index.js - Create Node Server
Create a Node Express server and it runs a port 3030. Here app.get method create a GET endpoint with /hello
const express = require('express');
});
const PORT = process.env.PORT || 3030;
const app = express();
app.get('/hello', (req, res, next) => {
res.send('Hello');
});
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log('Server is running on PORT:', PORT);
Start Server
npm run dev
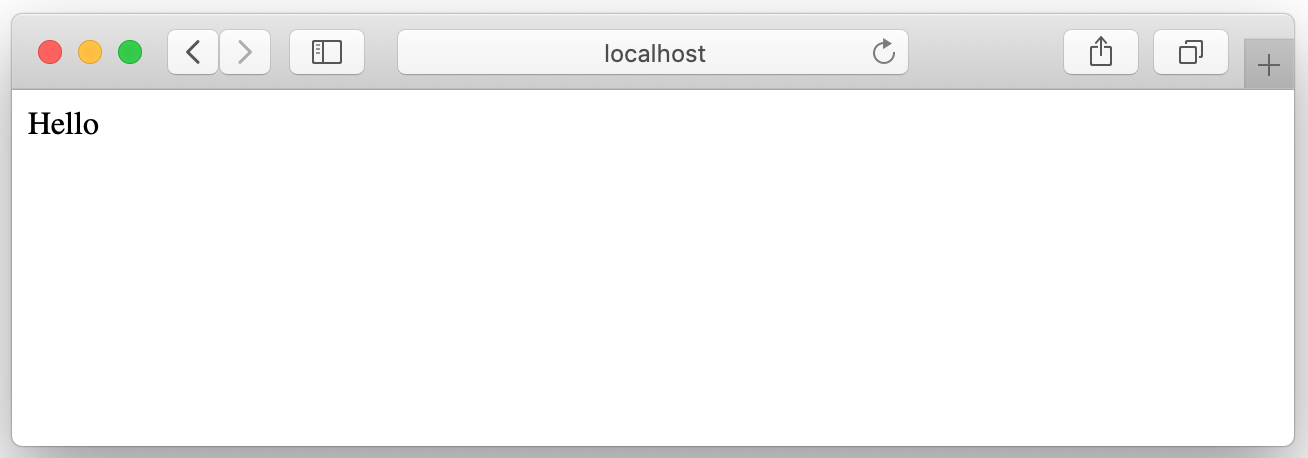
Run at http://localhost:3030/hello
Open the browser and hit the URL and you will find the following message.
Working with MySQL
Install the MySQL database and create the users and messages table. If you are using XAMPP, start the MySQL server.

queries.js
This file contains all of the queries methods and export the methods. Using MySQL connection getting all of the user's data with promise resolve.
const mysql = require('mysql');
const connection = mysql.createConnection({
host: 'localhost',
user: 'root',
password: '',
database: 'node',
});
const users = async () => {
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
connection.query('SELECT uid, username FROM users', function (
error,
data,
fields
) {
if (error) {
reject(err);
} else {
resolve(data);
}
});
});
return promise;
};
module.exports = {
users,
};
index.js
Import the queries.js and connect with /users GET restful endpoint.
const express = require('express');
});
const queries = require('./queries');
const PORT = process.env.PORT || 3030;
const app = express();
app.get('/hello', (req, res, next) => {
res.send('Hello');
});
app.get('/users', async (req, res, next) => {
try{
queries.users().then(data=>{
res.json(data);
})
} catch(err){
next(err)
}
});
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log('Server is running on PORT:', PORT);
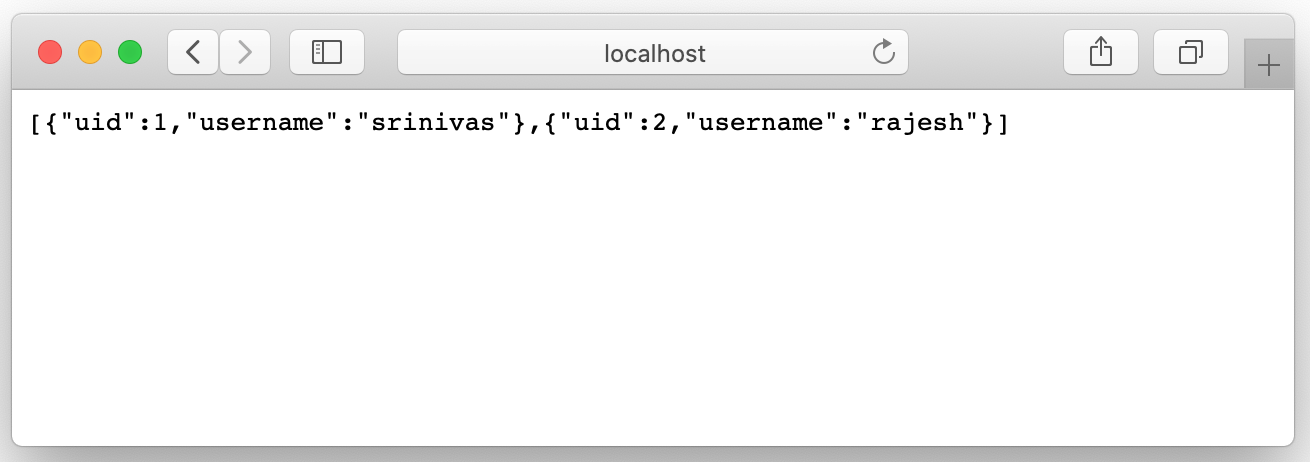
http://localhost:3030/users
You will access all the user's information from the database.
Request Params - http://localhost:3030/user/2
index.js
Express is allowing to access request parameters with routes. Here create an user endpoint with user id.
app.get('/user/:uid', async (req, res, next) => {
});
const uid = req.params.uid;
try{
queries.user(uid).then(data=>{
res.json(data);
})
} catch(err){
next(err)
}
queries.js
Create an another method to get the particular user details based on the user id.
const user = async (uid) => {
};
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
connection.query(
'SELECT uid, username, email FROM users WHERE uid = "' + uid + '"',
function (error, data, fields) {
if (error) {
reject(err);
} else {
resolve(data);
}
}
);
});
return promise;
POST-Restful Calls
Need a few more plugins to complete the POST requests.
body-parse
Request body JSON parsing middleware.
npm install body-parser
bcrypt
This plugin helps to encrypt the user password in a secure way.
npm install bcrypt
index.js - /signup
Create POST method and pass the req.body to queries.signup method.
const express = require('express');
});
const queries = require('./queries');
const PORT = process.env.PORT || 3030;
const app = express();
/* JSON body parse*/
const bodyParser = require('body-parser')
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: true }))
app.use(bodyParser.json())
app.get('/users', async (req, res, next) => {
...
...
});
app.get('/user/:uid', async (req, res, next) => {
...
...
});
app.post('/signup', async (req, res, next) => {
const postData = req.body;
try{
queries.signup(postData).then(data=>{
res.json({'status': 'success'});
})
} catch(err){
next(err)
}
});
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log('Server is running on PORT:', PORT);
queries.js -signup
Here assigning the postData values and encrypting the password with hash value. Insert statement insert the values into the database.
const mysql = require('mysql');
const bcrypt = require('bcrypt');
const connection = mysql.createConnection({
host: 'localhost',
user: 'root',
password: '',
database: 'node',
});
const users = async () => {
...
...
};
const user = async (uid) => {
...
...
};
const signup = async (postData) => {
const username = postData.username;
const email = postData. email ;
const password = postData.password;
const salt = bcrypt. genSaltSync ();
const encryptedPassword = bcrypt.hashSync(password, salt);
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
connection.query(
'INSERT INTO users (username,email,password) VALUES ("' +
username +
'","' +
email +
'","' +
encryptedPassword +
'")',
function (error, data, fields) {
if (error) {
reject(err);
} else {
resolve(data);
}
}
);
});
return promise;
};
module.exports = {
users,
user,
signup,
};
You need a postman application to test the POST request. Submit a JSON request with raw.
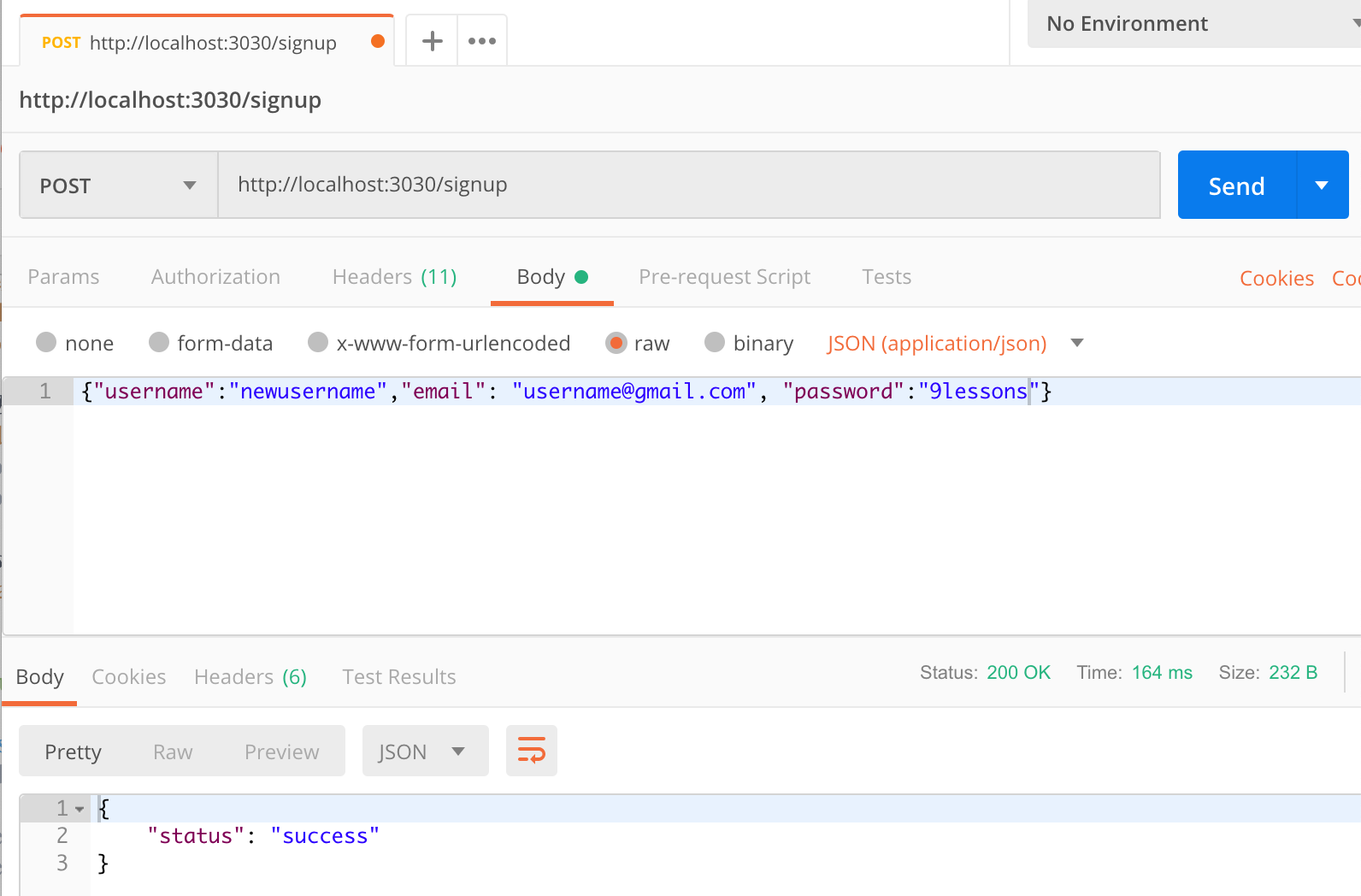
Request Body Validation
You have to apply request validations to protect the RESTful endpoints.
Express Validation
This is middleware validation and it can use JOI validation rules.
npm install express-validation
index.js - validation
You can apply validations with Joi methods.
const express = require('express');
/* Validation error status*/
const queries = require('./queries');
const PORT = process.env.PORT || 3030;
const app = express();
/* JSON body parse*/
const bodyParser = require('body-parser');
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: true }));
app.use(bodyParser.json());
/* Request validation */
const { validate, ValidationError, Joi } = require('express-validation');
app.get('/users', async (req, res, next) => {
try {
queries.users().then((data) => {
res.json(data);
});
} catch (err) {
res.json(err);
}
});
/ * yes validation * /
const uidValidation = {
params: Joi.object({
uid: Joi.number().integer().required(),
}),
};
app.get('/user/:uid', validate(uidValidation), async (req, res, next) => {
const uid = req.params.uid;
try {
queries.user(uid).then((data) => {
res.json(data);
});
} catch (err) {
res.json(err);
}
});
/* Signup validation*/
const signupValidation = {
body: Joi.object({
email: Joi.string().email().required(),
username: Joi.string().min(3).max(20).required(),
password: Joi.string().regex(/^[a-zA-Z0-9]{8,30}$/).required(),
}),
};
app.post('/signup', validate(signupValidation), async (req, res, next) => {
const postData = req.body;
try {
queries.signup(postData).then((data) => {
res.json({ status: 'success' });
});
} catch (err) {
res.json(err);
}
});
/* Validation error status*/
app.use(function (err, req, res, next) {
if (err instanceof ValidationError) {
return res.status(err.statusCode).json(err);
}
return res.status(500).json(err);
});
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log('Server is running on PORT:', PORT);
});
Email validation error
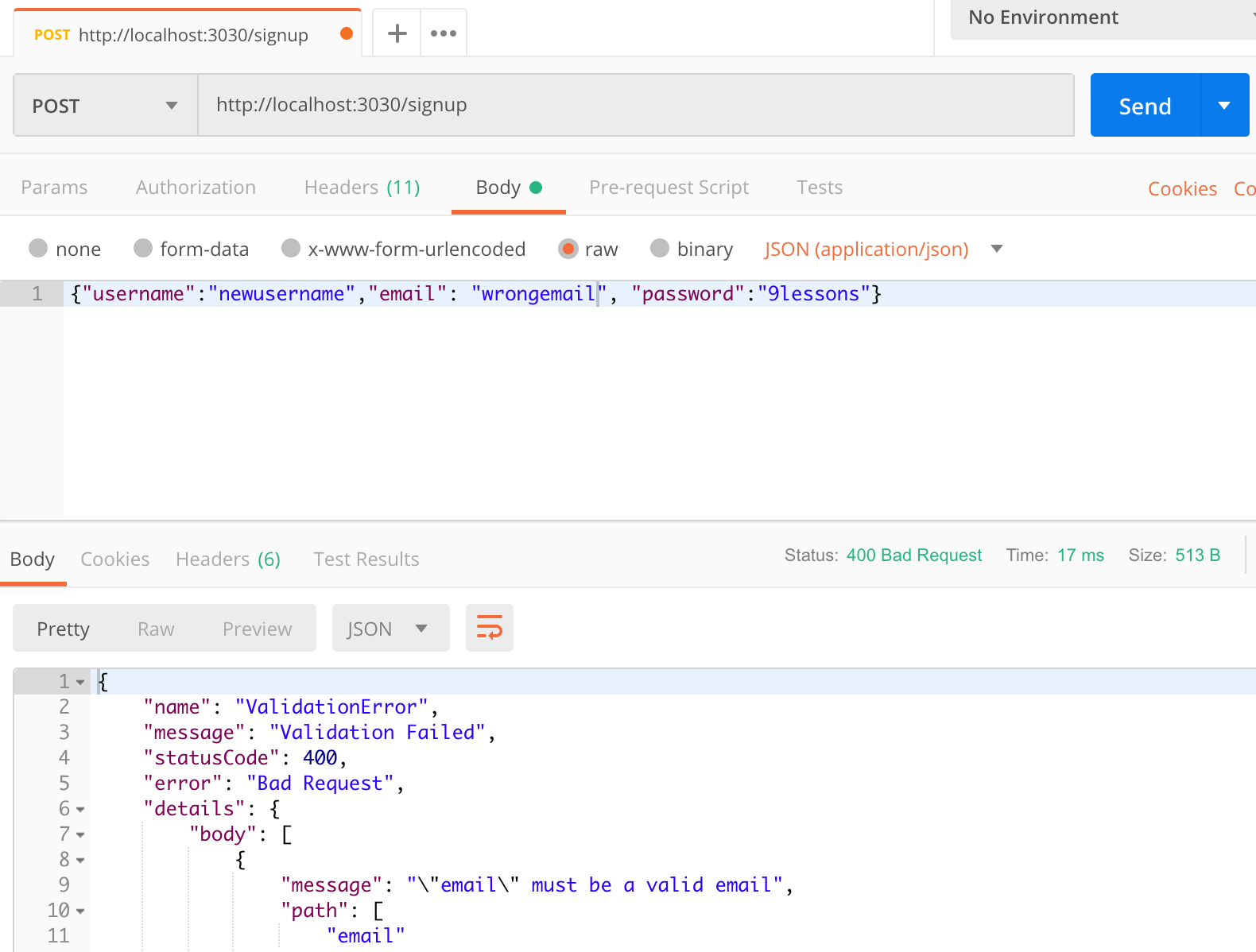
Note: You will find more endpoints in the GIT repository.
CORS on ExpressJS - Cross Domain
If you are deploying this on different domains, you have to allow origins to connect cross-domain. You can restrict the Access-Control-Allow-Origin value with your application domain. Here * means allowing all access point like Mobile, Desktop, etc.
/* CORS cross domain
});
* Replace * with your domain
*/
app.use(function(req, res, next) {
res.header("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "*");
res.header("Access-Control-Allow-Headers", "Origin, X-Requested-With, Content-Type, Accept");
next();
0 comments